Cryoablation for Pulmonary Nodule
Prevalent Lung Cancer and Worrisome Pulmonary Nodules
According to data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization, approximately 4.57 million new cancer cases were diagnosed in China in 2020, with lung cancer accounting for around 820,000 cases. Among the 31 provinces and cities in China, the incidence rate of lung cancer in males ranks first in all regions except for Gansu, Qinghai, Guangxi, Hainan, and Tibet, and the mortality rate is the highest regardless of gender. The overall incidence rate of pulmonary nodules in China is estimated to be around 10% to 20%, with a potentially higher prevalence among individuals over 40 years old. However, it should be noted that the majority of pulmonary nodules are benign lesions.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Nodules
Pulmonary nodules refer to focal round-shaped dense shadows in the lung, with various sizes and clear or blurred margins, and a diameter less than or equal to 3 cm.
Imaging Diagnosis: Currently, the targeted scanning imaging technique, known as ground-glass opacity nodule imaging diagnosis, is widely used. Some experts can achieve a pathological correlation rate of up to 95%.
Pathological Diagnosis: However, imaging diagnosis cannot replace tissue pathology diagnosis, especially in cases of tumor-specific precision treatment that requires molecular pathological diagnosis at the cellular level. Pathological diagnosis remains the gold standard.
Conventional Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Pulmonary Nodules
Percutaneous Biopsy: Tissue pathology diagnosis and molecular pathology diagnosis can be achieved under local anesthesia via percutaneous puncture. The average success rate of biopsy is about 63%, but complications such as pneumothorax and hemothorax may occur. This method only supports diagnosis and is difficult to perform concurrent treatment. There is also a risk of tumor cell shedding and metastasis. Conventional percutaneous biopsy provides limited tissue volume, making real-time tissue pathology diagnosis challenging.
General Anesthesia Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) Lobectomy: This approach allows for diagnosis and treatment simultaneously, with a success rate approaching 100%. However, this method may not be suitable for elderly patients or special populations who are intolerant to general anesthesia, patients with pulmonary nodules smaller than 8 mm in size or lower density (<-600), nodules located deep between arbitrary segments, and nodules in the mediastinal region near the hilar structures. Additionally, surgery may not be an appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic choice for situations involving postoperative recurrence, recurrent nodules, or metastatic tumors.
New Treatment Method for Pulmonary Nodules – Cryoablation
With the continuous development of medical technology, tumor treatment has entered the era of “precision diagnosis and precision treatment“. Today, we will introduce a local treatment method that is highly effective for non-malignant tumors and non-vascular proliferative pulmonary nodules, as well as early-stage tumor nodules (less than 2 cm) – cryoablation.
Cryotherapy
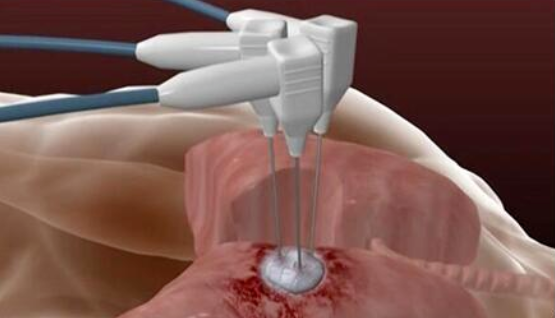
Ultra-low temperature cryoablation technique (cryotherapy), also known as cryosurgery or cryoablation, is a surgical medical technique that uses freezing to treat target tissues. Under CT guidance, precise positioning is achieved by puncturing the tumor tissue. After reaching the lesion, the local temperature at the site is rapidly decreased to -140°C to -170°C using argon gas within minutes, thereby achieving the goal of tumor ablation treatment.
Principle of Cryoablation for Pulmonary Nodules
1. Ice-crystal effect: This does not affect pathology and enables rapid intraoperative pathological diagnosis. Cryoablation physically kills tumor cells and causes microvascular occlusion.
2. Immunomodulatory effect: This achieves a distant immune response against the tumor. It promotes antigen release, activates the immune system, and relieves immune suppression.
3. Stabilization of mobile organs (such as lung and liver): This enhances the success rate of biopsy. A frozen ball is formed, making it easy to stabilize, and the edges are clear and visible on imaging. This patented application is simple and efficient.
Due to the two characteristics of cryoablation – “freezing anchoring and fixation effect” and “intact tissue structure after freezing without affecting pathological diagnosis”, it can assist in lung nodule biopsy, achieve real-time frozen pathological diagnosis during the procedure, and improve the success rate of biopsy. It is also known as “cryoablation for pulmonary nodule biopsy“.
Advantages of Cryoablation
1. Addressing respiratory disturbance: Local freezing stabilizes lung tissue (using coaxial or bypass freezing methods).
2. Addressing pneumothorax, hemoptysis, and risk of air embolism and tumor seeding: After forming a frozen ball, a closed negative pressure extracorporeal channel is established for diagnosis and treatment purposes.
3. Achieving concurrent on-site diagnosis and treatment goals: Cryoablation of the lung nodule is performed first, followed by re-warming and 360° multidirectional biopsy to increase the amount of biopsy tissue.
Although cryoablation is a method for local tumor control, some patients may exhibit a distant immune response. However, a large amount of data shows that when cryoablation is combined with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and other treatment methods, long-term tumor control can be achieved.
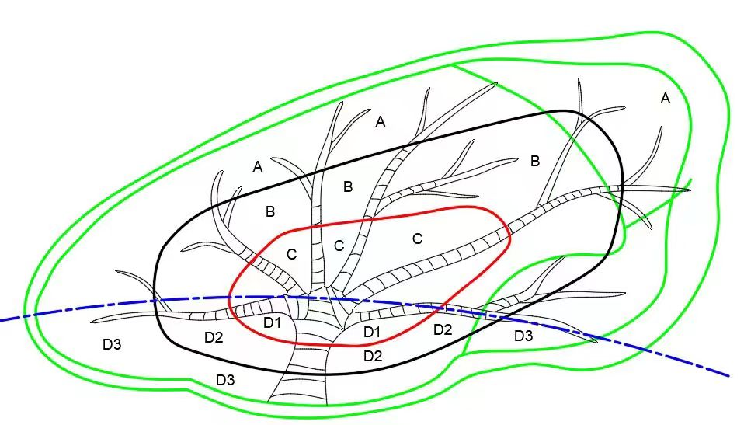
Indications for Percutaneous Cryoablation under CT Guidance
B-zone lung nodules: For lung nodules requiring segmental or multiple segmental resection, percutaneous cryoablation can provide a preoperative definitive diagnosis.
A-zone lung nodules: Bypass or oblique approach (the goal is to establish a lung tissue channel, preferably with a length of 2 cm).
Indications
Non-malignant tumors and non-vascular proliferative pulmonary nodules:
This includes precancerous lesions (atypical hyperplasia, in situ carcinoma), immune reactive proliferative lesions, inflammatory pseudotumors, localized cysts and abscesses, and proliferative scar nodules.
Early-stage tumor nodules:
Based on existing experience, cryoablation is also an effective treatment method comparable to surgical resection for ground-glass opacity nodules smaller than 2 cm with less than 25% solid component.
Post time: Sep-05-2023