-

Comprehensive Interpretation of CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell), which stands for chimeric antigen receptor T-cells, is a process where a person’s T cells are genetically engineered outside the body to be modified, giving them the ability to recognize and efficiently kill cancer cells before being re-infused into the patient’s body, thereby achieving the goal of treating malignant tumors.
In fact, CAR-T therapy is not only used for treating cancer but also holds great potential in the fields of autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, heart disease, and age-related diseases.
T cells, also known as T lymphocytes, are the main components of lymphocytes and are primarily responsible for immune responses and disease defense. They have functions such as directly killing target cells, assisting and inhibiting B cells to produce antibodies, responding to specific antigens and mitogens, and producing cytokines.
Of course, the human immune system is not limited to T cells; it also includes B cells, neutrophils, K cells, NK cells, and more. They play roles in clearing waste metabolic products from the body, recognizing and producing antibodies, and identifying and killing foreign pathogens and cancer cells.
Since T cells already have the function of recognizing and killing cancer cells, why is it necessary to artificially add CAR to T cells to create CAR-T cells to kill cancer cells? This brings us to the concept of immune evasion, which is one of the most fundamental characteristics of cancer.
CAR-T therapy, or CAR-T cell therapy, involves separating the patient’s T cells, expanding them outside the body, and then introducing an artificially designed tumor cell antigen CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) to the T cells. After processing, the anti-tumor activity of T lymphocytes is significantly enhanced before being re-infused into the patient’s body, thus restoring the T cells’ ability to recognize and kill cancer cells. This is the essence of CAR-T cell therapy.
Impact Bio’s CAR-T therapy IMPT-514 receives FDA approval.
On August 21, 2024, Impact Bio announced that the FDA had approved its IND application for the IMPT-514 therapy it developed. IMPT-514 is a bispecific CD19/CD20 CAR-T therapy used to treat active refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In clinical trial data, IMPT-514 was shown to be highly efficient in producing from patients with severe immunosuppression from various autoimmune diseases, and it demonstrated potent autologous B-cell clearance capabilities with a mild cytokine profile. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR-T therapy for large B-cell lymphoma still shows sustained response after five years. On August 2, 2024, the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) released a data report on long-term survival rates following CAR-T cell therapy. The results showed that among patients who underwent CAR-T therapy, the 5-year progression-free survival rate was 29%, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate was 40%, and the 5-year lymphoma-specific survival rate was 53%, with rare late relapses. Axicabtagene ciloleucel is an autologous CD19 chimeric antigen receptor CAR-T cell therapy approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Conclusion: In a standard care setting, the treatment outcomes of axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR-T are consistent with the results reported in clinical trials, with sustained, durable responses observed at the 5-year mark.
World’s first successful CAR-T treatment for autoimmune disease.On October 4, 2024, the Nature website headlined a report introducing a research outcome from a Chinese team. Scientists used CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology to genetically engineer healthy donor-derived CAR-T cells targeting CD19, developing a new generation of allogeneic universal CAR-T therapy that helped three patients with severe autoimmune diseases achieve long-term remission.
-
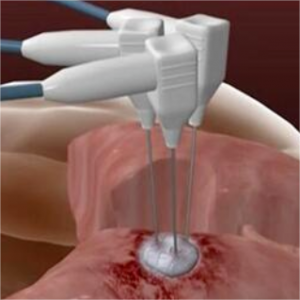
“Lung nodule cryoablation” ice-breaking medical problems
The routine management of pulmonary nodules includes biopsy and pneumonectomy.
Complications such as pneumothorax and hemothorax are easy to occur during biopsy.
There are risks of tumor cell shedding and metastasis. It is difficult to realize diagnosis because of the small amount of routine biopsy tissue.
-

Cervix Cancer
Cervical cancer, also known as cervical cancer, is the most common gynecological tumor in the female reproductive tract. HPV is the most important risk factor for the disease. Cervical cancer can be prevented through regular screening and vaccination. Early cervical cancer is highly cured and the prognosis is relatively good.
-

Renal Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating from the urinary tubular epithelial system of the renal parenchyma. The academic term is renal cell carcinoma, also known as renal adenocarcinoma, referred to as renal cell carcinoma. It includes various subtypes of renal cell carcinoma originating from different parts of the urinary tubule, but does not include tumors originating from the renal interstitium and renal pelvis tumors. As early as 1883, Grawitz, a German pathologist, saw that... -

Digestive Tract Cancer
In the early stage of digestive tract tumor, there are no uncomfortable symptoms and no obvious pain, but red blood cells in stool can be found through routine stool examination and occult blood test, indicating intestinal bleeding. Gastroscopy can find prominent new organisms in the intestinal tract in the early stage.
-
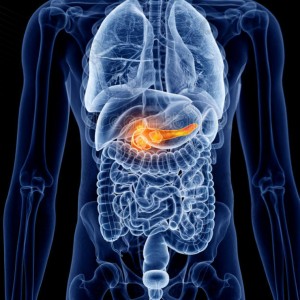
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers that affect the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach. It occurs when abnormal cells in the pancreas start to grow out of control, forming a tumor. The early stages of pancreatic cancer usually do not cause any symptoms. As the tumor grows, it can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, back pain, weight loss, loss of appetite, and jaundice. These symptoms can be caused by other conditions as well, so it is important to see a doctor if you experience any of them.
-

Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a common malignant tumor that is usually found when prostate cancer cells grow and spread in the male body, and its incidence increases with age. Although early diagnosis and treatment are very important, some treatments can still help slow the progression of the disease and improve the survival rate of patients. Prostate cancer can occur at any age, but it is usually the most common in men over the age of 60. Most prostate cancer patients are men, but there may also be women and homosexuals.
-

Ovarian Cancer
The ovary is one of the important internal reproductive organs of women, and also the main sexual organ of women. Its function is to produce eggs and synthesize and secrete hormones. with a high incidence rate among women. It seriously threatens women’s lives and health.
-

Carcinomaofrectum
Carcinomaofrectum is referred to as colorectal cancer, is a common malignant tumor in the gastrointestinal tract, the incidence is second only to stomach and esophageal cancer, is the most common part of colorectal cancer (about 60%). The vast majority of patients are over 40 years old, and about 15% are under 30 years old. Male is more common, the ratio of male to female is 2-3:1 according to clinical observation, it is found that part of colorectal cancer occurs from rectal polyps or schistosomiasis; chronic inflammation of the intestine, some can induce canceration; high-fat and high-protein diet causes an increase in cholic acid secretion, the latter is decomposed into unsaturated polycyclic hydrocarbons by intestinal anaerobes, which can also cause cancer.
-

Lung cancer
Lung cancer (also known as bronchial cancer) is a malignant lung cancer caused by bronchial epithelial tissue of different caliber. According to the appearance, it is divided into central, peripheral and large (mixed).
-

Liver Cancer
What is liver cancer? First, let’s learn about a disease called cancer. Under normal conditions, cells grow, divide, and replace old cells to die. This is a well-organized process with a clear control mechanism. Sometimes this process is destroyed and begins to produce cells that the body does not need. The result is that the tumor can be benign or malignant. A benign tumor is not a cancer. They will not spread to other organs of the body, nor will they grow again after surgery. Althoug... -
Bone Cancer
What is bone cancer? This is a unique bearing structure, frame, and human skeleton. However, even this seemingly solid system may be marginalized and become a refuge for malignant tumors. Malignant tumors can develop independently and can also be generated through the regeneration of benign tumors. In most cases, if we talk about bone cancer, we mean the so-called metastatic cancer, when the tumor develops in other organs (lung, breast, prostate) and spreads in the late stage, including bone ...
